Spring Cloud
微服务产生的背景
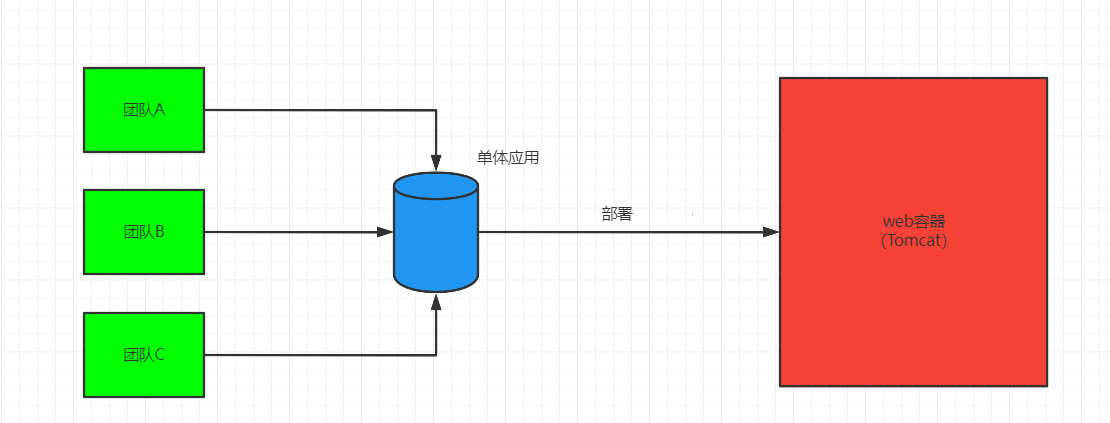
单体应用存在的问题:
- 随着业务的发展,开发变得越来越复杂。
- 修改、新增某个功能,需要对整个系统进行测试,重新部署。
- 一个模块出现问题,很可能导致整个系统崩溃。
- 多团队同时对数据进行管理,容易产生安全漏洞。
- 各个模块使用同一种技术框架,局限性太大,很难根据业务选择最适合的技术架构。
- 模块内容太复杂,如果员工离职,可能需要很长时间才能完成任务交接。
为了解决上述问题,微服务架构应运而生,简单来说,微服务就是将一个单体应用拆分成若干个小型服务,协同完成系统功能的一种架构模式,在系统架构层面进行解耦合,将一个复杂问题拆分成若干个简单问题。
这样的好处是对于每一个简单问题,开发、维护部署的难度就降低了很多,可以实现自治,可以自主选择最适合的技术框架,提高了项目开发的灵活性。
微服务架构不仅是简单的拆分,拆分之后的各个微服务之间还要进行通信,否则就无法协同完成需求。
微服务之间只需要制定统一的协议即可,至于每个微服务使用什么技术框架来完成,统统不需要关心。
这种松耦合的方式使开发、部署都变得更加灵活,同时系统更容易拓展,降低了开发、运维的难度。

微服务的优点
- 各个服务之间实现了松耦合,彼此之间不需要关注对方是用什么语言开发,什么技术开发,只需要保证自己的接口可以正常访问即可,通过标准协议访问其他接口即可。
- 各个微服务之间独立自治,只需要专注于做好自己的业务,开发和维护不会影响到其他的微服务。
- 微服务是一种去中心化的架构方式,相当于用零件拼接一台机器,如果某个零件出现问题,可以随时进行替换,从而保证机器的正常运行。
微服务的不足
- 如果某个系统的远程调用出现问题,导致微服务不可用,就有可能产生级联反应,造成整个系统的崩溃。
- 如果某个需求需要调用多个微服务,如何来保证数据的一致性。
- 相比较与单体应用,微服务的学习难度会增加,对于新加入团队的员工来讲,如何快速掌握上手微服务架构,是一个问题。
微服务设计原则
从大到小,提炼出核心需求,搞清楚服务间的交互关系,先拆分成粒度较大的服务,然后再根据具体的业务需求逐步细化服务粒度,最终形成一套合理的微服务系统架构。
- 服务粒度不能太小也不能太大,提炼核心需求,根据服务间的交互关系找到最合理的服务粒度。
- 各个微服务的功能和职责尽量单一,避免出现多个服务处理同一个需求。
- 各个微服务之间要相互独立、自治,自主开发、自主测试、自主部署、自主维护。
- 保证数据的独立性,各个微服务独立管理其业务模型下的数据。
- 使用RESTful协议完成微服务之间的写作任务,数据交互采用JSON格式,方便调用和整合。
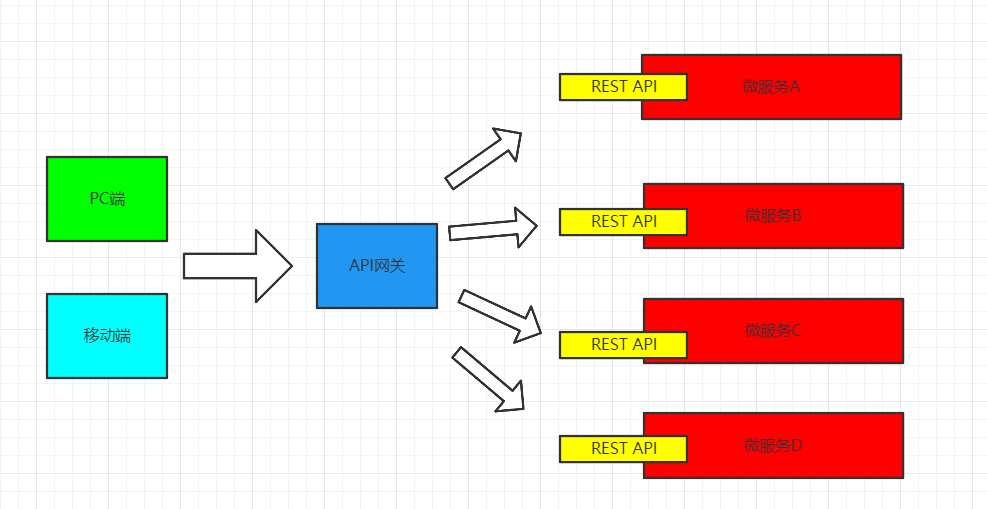
微服务架构的核心组件
- 服务治理
- 服务注册
- 服务发现
提供服务的叫做服务提供者。调用服务的叫做服务消费者。
- 服务负载均衡
- 服务网关
- 微服务容错机制
- 分布式配置
- 服务监控
解决方案
Spring Cloud
微服务是一种分布式软件架构设计方式,具体的落地方案有很多,Dubbo、Spring Boot/Spring Cloud、Motan等等,Spring Cloud基于Spring Boot使得整体的开发、配置、部署都非常方便,可以快速搭建基于微服务的分布式应用,Spring Cloud相当于微服务各个组件的集大成者。
Spring Boot和Spring Cloud的关系
Spring Boot快速搭建基础系统,Spring Cloud在此基础上实现分布式系统中的公共组件,如服务注册、服务发现、配置管理、熔断器、控制总线等,服务调用方式是基于REST API。
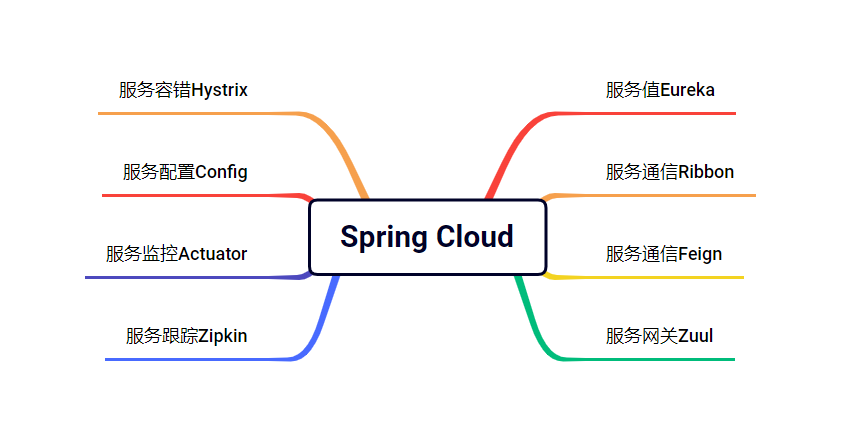
搭建微服务系统的核心中枢
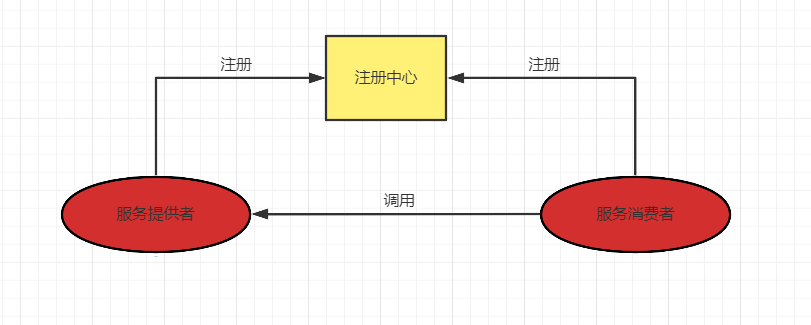
服务治理的核心组件:
- 服务提供者
- 服务消费者
- 注册中心
分布式系统架构中,每个微服务在启动时,将自己的信息存储再注册中心,服务注册。
服务消费者从注册中心查询服务提供者的网络信息,并通过此信息调用服务提供者的接口,服务发现。
注册中心管理各个微服务:通过心跳机制,每隔一定的时间微服务会向注册中心进行汇报,如果注册中心长时间无法与某个微服务通信,就会自动销毁该服务。
当某个微服务的网络信息发生变化是,也会重新注册。
服务提供者、服务消费者、注册中心的关联:
- 启动注册中心
- 服务提供者启动时,在注册中心可注册一个可以提供服务的实例。
- 服务消费者启动,在注册中心订阅需要调用的服务。
- 注册中心将服务提供者的信息推送给服务消费者。
- 服务消费者通过相关信息(IP、端口)调用服务提供者的服务。
注册中心核心模块:
- 服务注册表
- 服务注册
- 服务发现
- 服务检查(通过心跳机制完成各个微服务之间的通信)
Spring Cloud的服务治理可以使用Eureka组件。
什么是Eureka?
Spring Cloud Eureka,提供服务注册和服务发现的功能。
Spring Cloud Eureka的组成
Eureka Server 服务端
Eureka Client 客户端
代码实现
- 创建Maven父工程,pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.sfx</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
</project>- 在父工程目录下创建Module,实现Eureka Server,pom.xml。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- application.yml
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
client:
# 是否将当前的eureka服务作为客户端注册进去(是否注册自己)
register-with-eureka: false
# 获取其他eureka数据信息
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/- 创建启动类
package com.sfx;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class,args);
}
}- 启动,访问 http://localhost:8761 ,可以看到如下界面,启动成功。
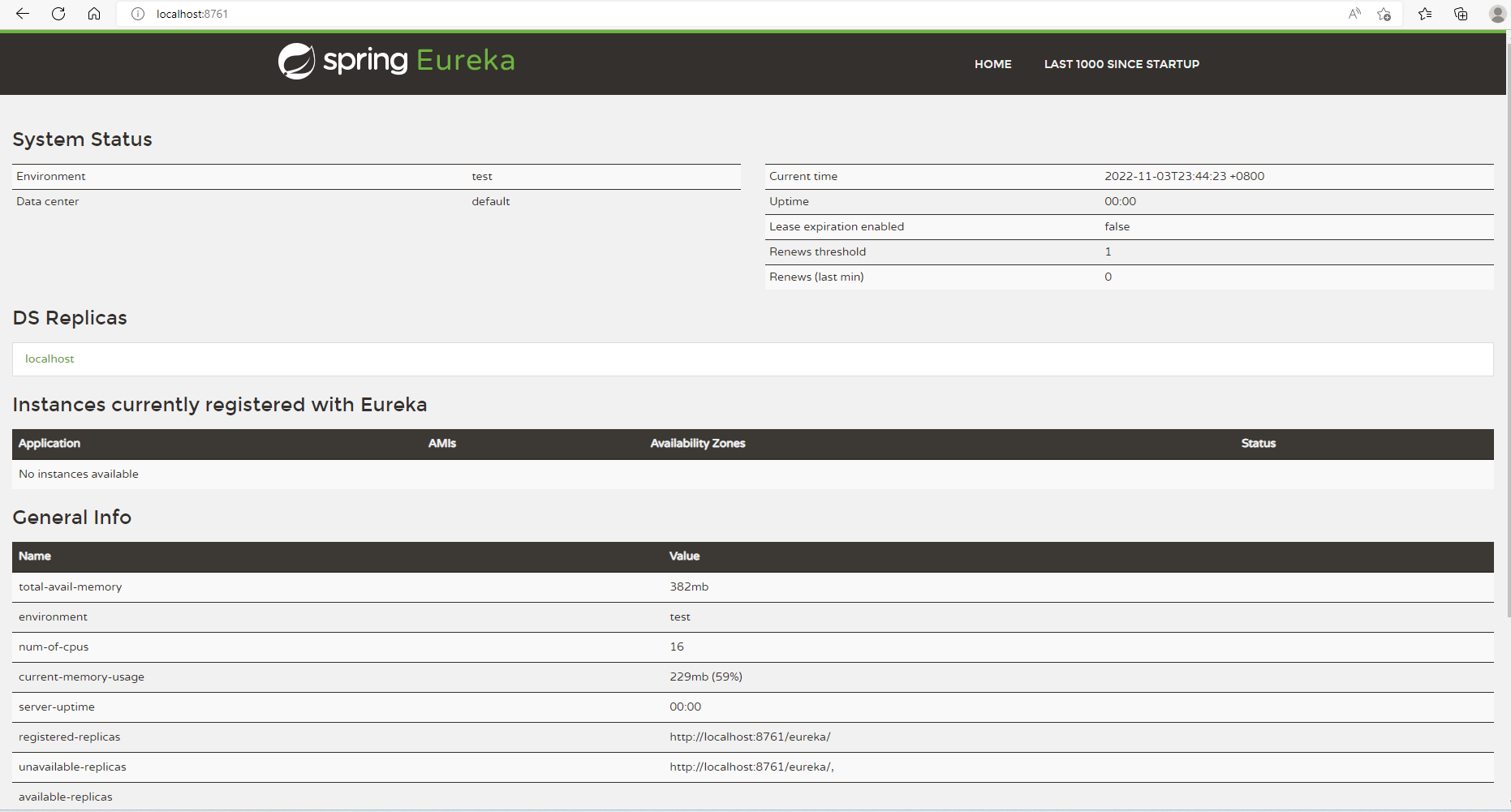
注册第一个微服务
服务提供者和服务消费者都是通过Eureka Client连接到Eureka Server完成注册。
1.创建Modelu,实现Eureka Clinet。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- application.yml
server:
port: 8010
spring:
application:
name: provider
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
# 是否注册ip地址
prefer-ip-address: true- 创建启动类
package com.sfx;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class,args);
}
}- 创建实体类
package com.sfx.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
- 创建Repository
接口
package com.sfx.repository;
import com.sfx.entity.Student;
import java.util.Collection;
public interface StudentRepository {
public Collection<Student> findAll();
public Student findById(Integer id);
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student);
public void deleteById(Integer id);
}实现类
package com.sfx.repository.impl;
import com.sfx.entity.Student;
import com.sfx.repository.StudentRepository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class StudentRepositoryImpl implements StudentRepository {
private static Map<Integer,Student> map;
static {
map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,new Student(1,"张三"));
map.put(2,new Student(2,"李四"));
map.put(3,new Student(3,"王五"));
}
@Override
public Collection<Student> findAll() {
return map.values();
}
@Override
public Student findById(Integer id) {
return map.get(id);
}
@Override
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student) {
map.put(student.getId(),student);
}
@Override
public void deleteById(Integer id) {
map.remove(id);
}
}- StudentHandler
package com.sfx.controller;
import com.sfx.entity.Student;
import com.sfx.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/provider")
public class StudentHandler {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection<Student> findAll(){
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return studentRepository.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}接口测试
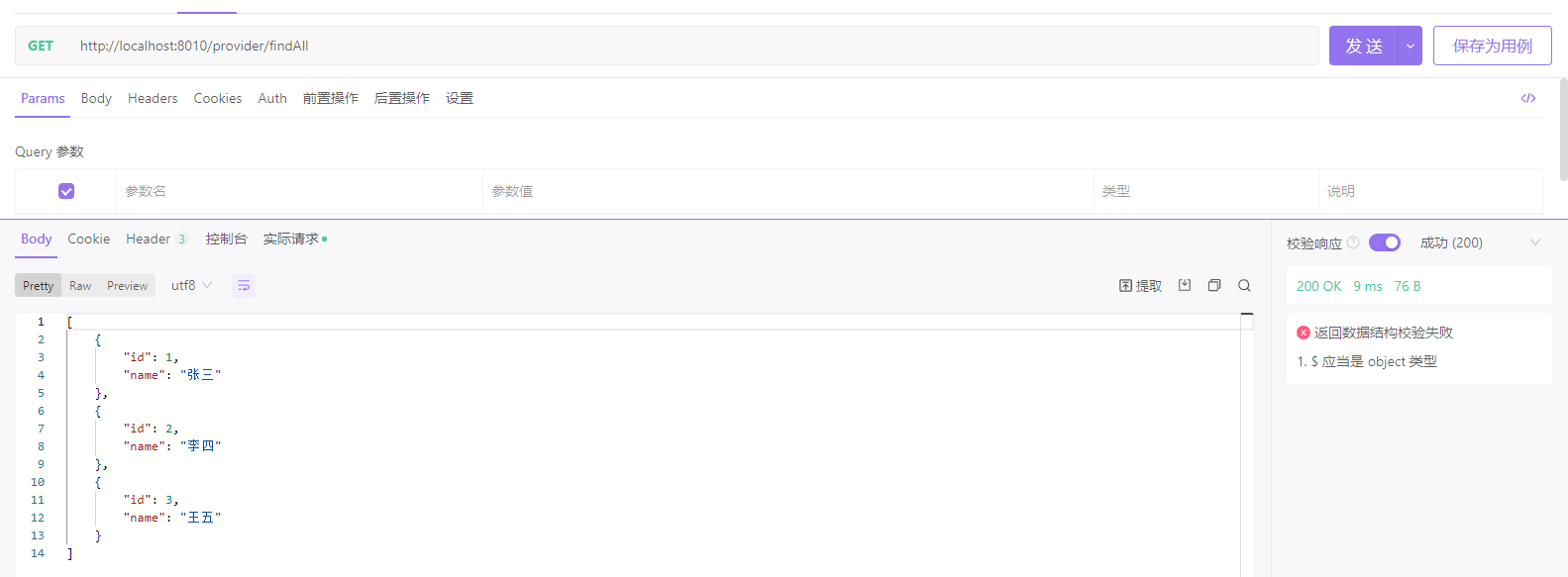
RestTemplate
通过RestTemplate可以实现不同微服务之间的调用。
RestTemplate是Spring框架提供的一种基于RESTful的服务组件,底层对HTTP请求及相应进行了封装,提供了很多访问远程REST服务的方法,可以简化代码的开发。
如何使用RestTemplate
- 创建Maven工程,pom.xml
<parent> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <version>2.7.3</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> - 创建User类